interest tax shield explained
A tax shield is the reduction in income taxes that results from taking an allowable deduction from taxable income. Interest tax shield refers to the reduction in taxable income which results from allowability of interest expense as a deduction from taxable income.

Home Tax Shield Launches Property Tax Protest Software San Antonio Business Journal
Moreover this must be noted that interest tax shield value is the present value of all the interest tax shield.
. The interest tax shield is positive when the EBIT is greater than the payment of interest. Tax shields differ between countries and are based on what deductions are eligible versus ineligible. The value of a company is based on the total value available to all investors.
A Tax Shield is an allowable deduction from taxable income that results in a reduction of taxes owed. Basically the company uses two main tax shield strategies. Interest payments on loans are deductible meaning that they reduce the taxable income.
Thus if the tax rate is 21 and the business has. An interest tax shield refers to the tax savings made by a company as a direct result of its debt interest payments. Interest Tax Shield A reduction in tax liability coming from the ability to deduct interest payments from ones taxable income.
A Tax Shield is an allowable deduction from taxable income that results in a reduction of taxes owed. A tax shield is a reduction in taxable income for an individual or corporation achieved through claiming allowable deductions such as mortgage interest medical expenses charitable donations. While tax shields are used for tax savings for both personal and business tax returns this article focuses on tax shields for businesses.
The total cash available to both. Interest Tax Shield Formula Average debt Cost of debt Tax rate. Because of tax shields it is necessary to adjust the cost of debt when comparing it to the cost of equity.
A tax shield refers to deductions taxpayers can take to lower their taxable income. As is hopefully clear by this stage the interest tax shield is just one example of the tax shielding opportunities available to companies. Interest expenses via loans and mortgages are tax-deductible meaning they lower the taxable income.
Interest tax shields refer to the reduction in the tax liability due to the interest expenses. The second expression in the second equation CI CO D t calculates depreciation tax shield separately and subtracts it from pre-tax net cash flows CI CO. The reduction in income taxes that results from the tax-deductibility of interest payments.
The calculation of depreciation tax shield can be obtained by depreciation expense and tax rate as shown below Depreciation Tax Shield Formula Depreciation expense Tax rate Table of contents Formula to Calculate Tax Shield Depreciation Interest. Tax shields are favored by wealthy individuals and corporations but middle-class individuals can benefit from tax shields as well. A tax shield is a reduction in taxable income for an individual or corporation achieved through claiming allowable deduction as mortgage interest Deduction As Mortgage Interest Mortgage interest deduction refers to the decrease in taxable income allowed to the homeowners for their interest on a home loan taken for purchase or construction of the house or any borrowings.
What is a Tax Shield. Thus interest expenses act as a shield against tax obligations. Interest Tax Shield A reduction in tax liability coming from the ability to deduct interest payments from ones taxable income.
In addition interest expense after refinancing will be CH ¼ 395 51 ¼ 0775. 1 1 - t Where t. Examples of tax shields include deductions for charitable contributions mortgage deductions medical expenses and depreciation.
The person gets the benefits while he offsets his taxable. Stated another way its the deliberate use of taxable expenses to offset taxable income. The value of a tax shield is calculated as the amount of the taxable expense multiplied by the tax rate.
An interest tax shield approach is useful for individuals who want to purchase a house with a mortgage or loan. A tax shield is a reduction in taxable income by taking allowable deductions. Equity and debt holders and therefore the tax shield increases the value of the company.
For example a mortgage provides an interest tax shield for a property buyer because interest on mortgages is generally deductible. For example a mortgage provides an interest tax shield for a property buyer because interest on mortgages is generally deductible. Companies pay taxes on the income they generate.
This interest payment therefore acts as a shield to the tax obligation. 1 For example because interest on debt is a tax-deductible expense taking on debt creates a tax shield. Using a risk-free rate of 4 a discount rate for EBIT of 12 and a tax rate of 36 we estimate the value of tax shields to be 627 billion.
The impact of adding removing a tax shield is highly impacted by the companys optimal capital structure which is a mix of debt and equity fundingMoreover the interest expense on the debt is tax deductible which makes the. Obviously a company makes money from interest income related to investments. The use of fixed assets as a tax shield encourages businesses to make further investments in their operations which may make them more competitive and profitable.
The value of these shields depends on the effective tax rate for the corporation or individual being subject to a higher rate increases the value of the deductions. Click here to learn more about this topic. With that value the refinancing barrier is K 14 9 282 395.
A typical tax shield adjustment is that usually done in WACC calculations where the usual approach is to multiply the interest rate by. A tax shield is the tax saving made by using debt rather than equity. How to Calculate a Tax Shield Amount.
------------------------------------- tax shield is the saving in taxable income for individualscorporations by cutting the expansible allowance such as depreciation mortgage interests hospital.
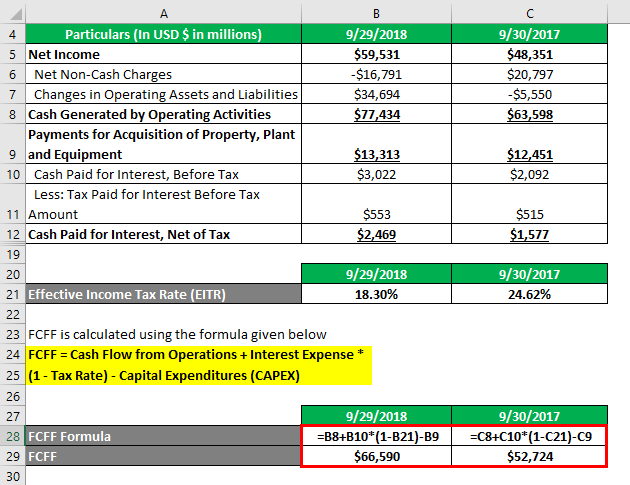
Fcff Formula Examples Of Fcff With Excel Template
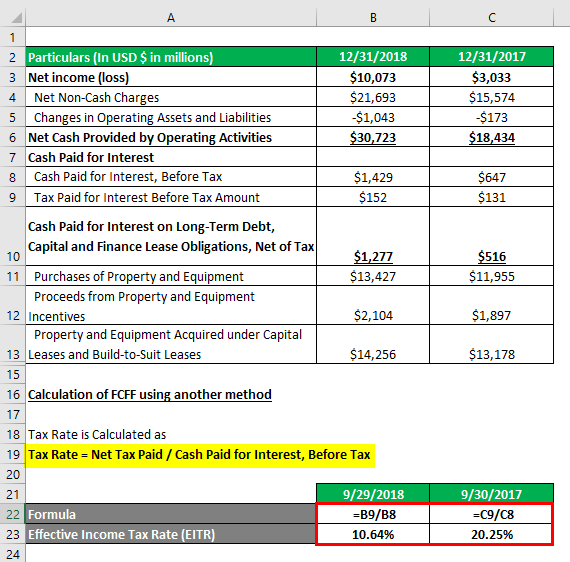
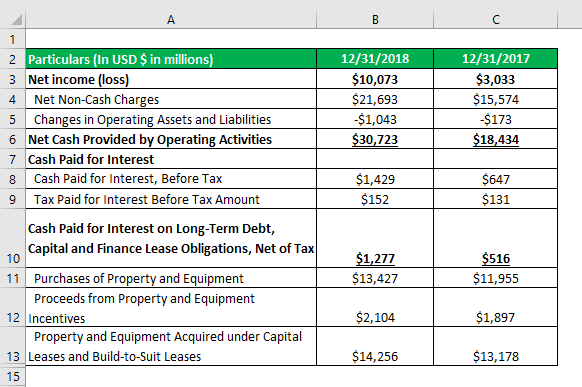
Fcff Formula Examples Of Fcff With Excel Template

Leverage Ratio Formula And Excel Calculator
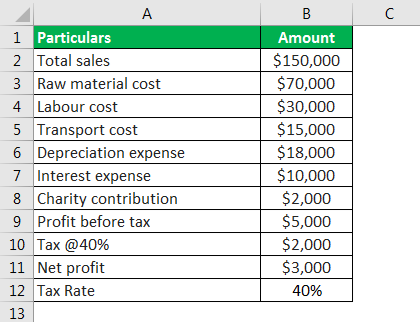
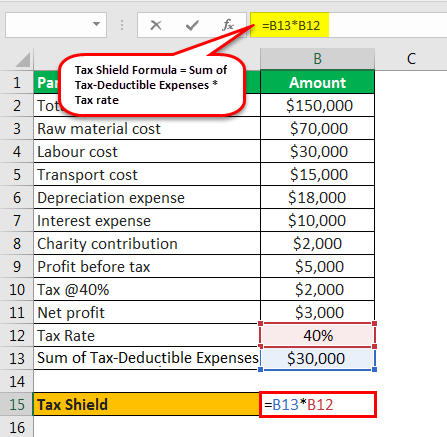
Tax Shield Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples
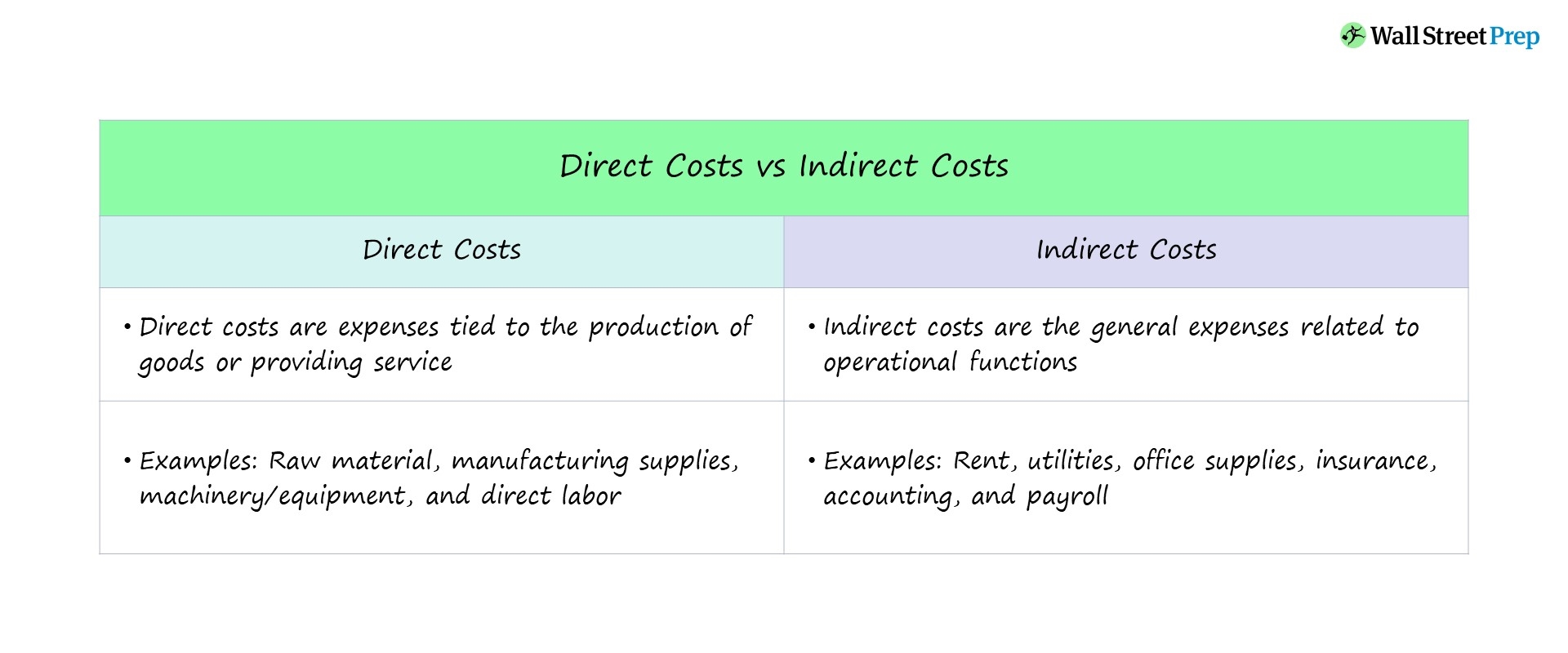
Direct Vs Indirect Costs Definition Differences Examples
Corporation Income Taxes And The Cost Of Capital A Revision
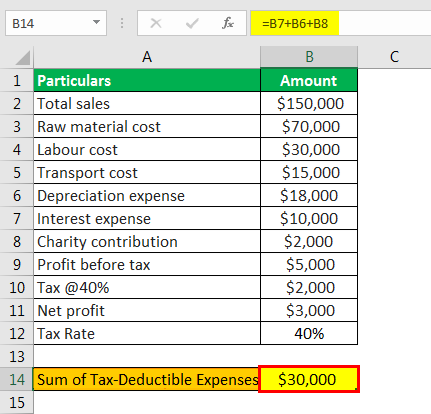
Tax Shield Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples
Corporation Income Taxes And The Cost Of Capital A Revision
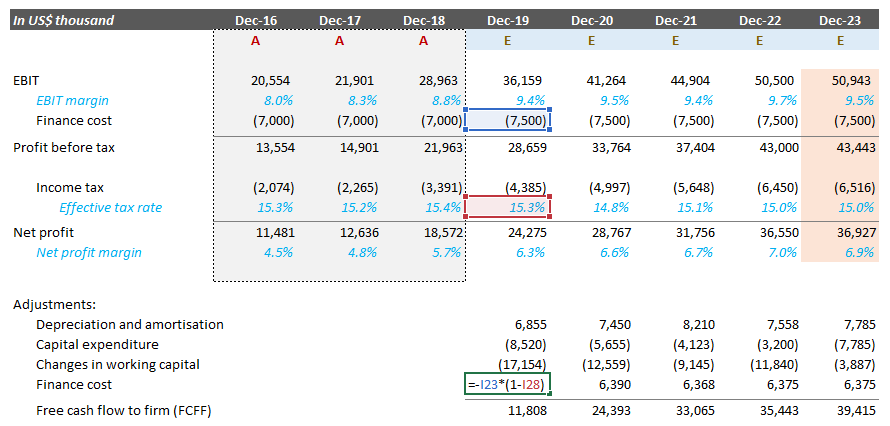
Step By Step Guide On Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Model Fair Value Academy

Leverage Ratio Formula And Excel Calculator

Fcff Formula Examples Of Fcff With Excel Template
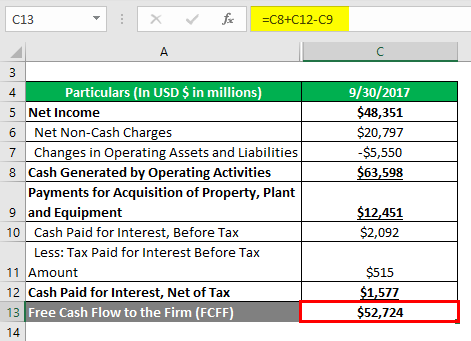
Fcff Formula Examples Of Fcff With Excel Template
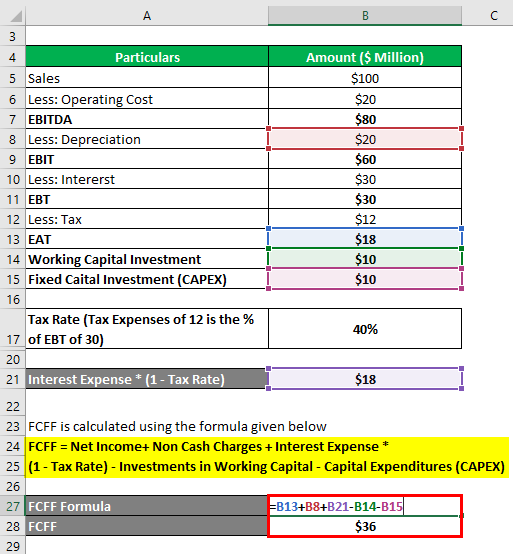
Fcff Formula Examples Of Fcff With Excel Template

Tax Shield Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples
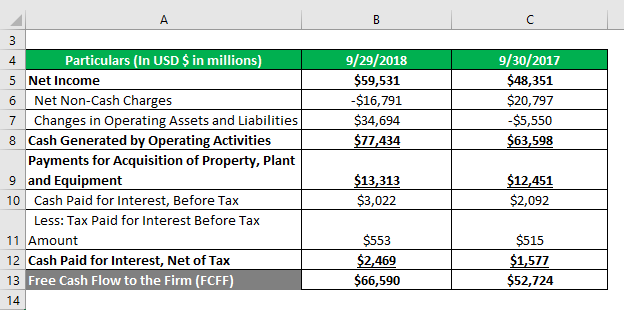
Fcff Formula Examples Of Fcff With Excel Template
Analyzing A Bank S Financial Statements

Leverage Ratio Formula And Excel Calculator